A new possible variant of Lichen Planopilaris - actinic LPP
Actinic Lichen Planopilaris (aLPP)
Authors of a new study report a new subtype of lichen planopilaris – known as actinic LPP.
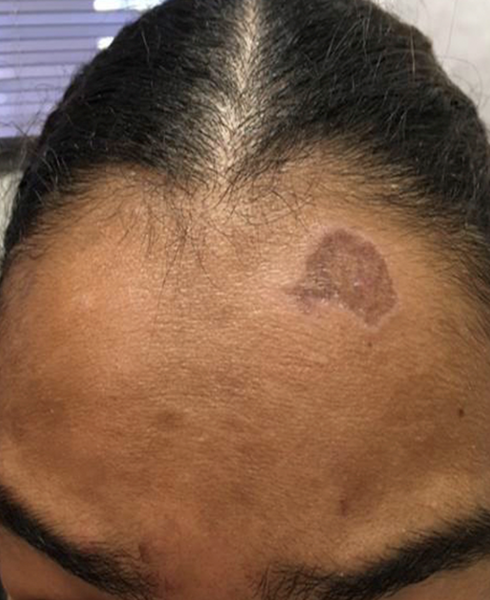
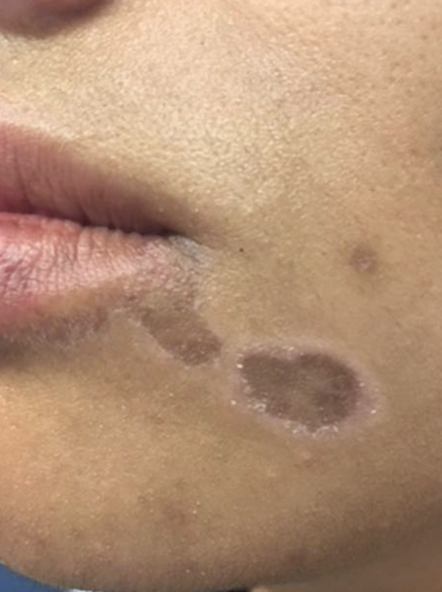
They present the case of a 39-year-old Sri Lankan woman with Fitzpatrick skin type V who presented with a 3-year history of pruritic, hyperpigmented plaques affecting sun-exposed sites. These sites included the face, dorsa of the hands and feet. Two punch biopsies confirmed the diagnosis of lichen planus and overall a diagnosis of actinic LP was felt to be appropriate. Treatment with mometasone furoate 0·1% ointment, tacrolimus 0·1% ointment and photoprotection using sunscreen led to a clinical improvement.
Two years later, the patient returned with symptoms of scalp discomfort and itching and longitudinal nail ridging. Her scalp itching was noticeably worse on sunny days and mostly affected the scalp along the parting line. She also reported worsening of her scalp symptoms during summer months and improvement in winter.
Trichoscopy revealed perifollicular scales and perifollicular erythema involving follicles near the scalp parting line. Scalp biopsies confirmed a diagnosis of LPP
In view of the clinicopathological findings, the term ‘actinic lichen planopilaris’ (aLPP) was used to describe the patient’s presentation. Treatment with high-potency topical corticosteroids and adherence to strict photoprotection proved effective in alleviating inflammatory symptoms and signs.
Actinic LP is a rare photosensitive variant of LP that tends to affect younger patients with darker skin types. Children and young adults are often affected. Actinic lichen planus (ALP) is also known as lichen planus subtropicus, lichen planus tropicus, summertime actinic lichenoid eruption, lichen planus atrophicus annularis, and lichenoid melanodermatosis
The exact cause of actinic LP is not clear although it may have an underlying genetic predisposition given its higher prevalence in patients of East African, Middle Eastern and Indian origin. Patients with actinic LPP have LP on sun-exposed areas and flare in summertime and experience remission in winter. Most patients with actinic LP do not have mucosal or nail involvement.
An example of actinic lichen planus. From: Kim T et al. Oral prednisone: A unique and effective treatment for actinic lichen planus. JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Oct 29;4(10):976-978. used with creative commons license.
Actinic lichen planus. From: Kim T et al. Oral prednisone: A unique and effective treatment for actinic lichen planus. JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Oct 29;4(10):976-978. used with creative commons license.
Summary
All in all, this patient had features of actinic LP and actinic LPP. Her LP was itchy although most with actinic LP do not have itching or it is mild. She had nail ridging although it’s not clear if this was truly nail LP or not. Most patients with actinic LP do not have nail involvement.
REFERENCE
Lalagianni N et al. Actinic lichen planopilaris: a new variant of lichen planopilaris triggered by ultraviolet radiation. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2023 Feb 2;48(2):158-160.
This article was written by Dr. Jeff Donovan, a Canadian and US board certified dermatologist specializing exclusively in hair loss.