Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis From Topical Minoxidil : A new mechanism of minoxidil induced red scalp?
Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis From Topical Minoxidil : A new mechanism of minoxidil induced red scalp?
Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP) is a rare skin reaction characterized by the sudden onset of multiple, small, sterile, non-follicular typically pin-head sized pustules in an erythematous and edematous base succeeding systemic drug administration. It may rarely occur from direct application of medications. It is usually accompanied by fever and neutrophilic leukocytosis.
Makris M et al. 2023
In a new report, authors from Greece describe what they feel is the first case of ALEP attributed to minoxidil in a female patient with androgenetic alopecia.
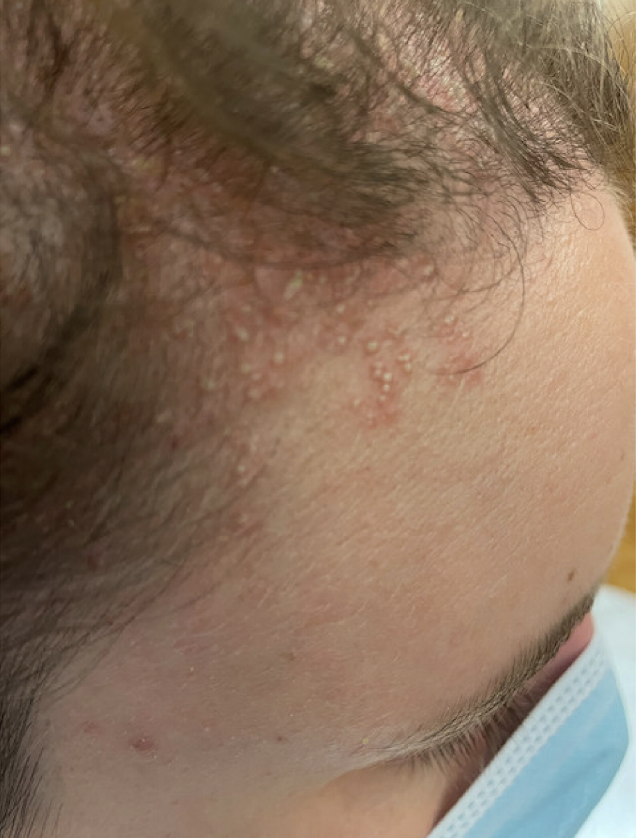
The patient was a 31-year-old white female with androgenetic alopecia presented to the Emergency Department with concerns related to a sudden outbreak of multiple itchy pustules on the frontal scalp, forehead, and neck. The eruptions appeared about 48 h after the application of a special compounded foam formulation containing 17-alpha-estradiol 0.05% and minoxidil 5%.
In was noted by the authors that in prior years, the patient had developed a mild, pustular-free, pruritic eruption on the scalp after topical application of minoxidil. This fully resolved without treatment within four days after the cessation of minoxidil application.
At her visit to the Emergency Department, examination of the skin showed multiple non-follicular pustules affecting the scalp, forehead, and neck on an erythematous, edematous background. She had enlarged cervical lymph nodes were noted, with the patient being nearly febrile (temperature of 37.8 ◦C). She had no mucosal or joint involvement. Blood tests were normal. Bacterial and fungal blood cultures were negative and Herpes Simplex Virus serology was also negative.
Pustular reaction in a patient using topical minoxidil. FROM: Makris et al. Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP) Caused by Topical Application of Minoxidil. J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 20;12(3):831.
The minoxidil-estradiol formulation was immediately discontinued, and the patient was treated with potent topical steroids. Resolution of the pustular lesions occurred within seven days.
The patient had patch testing at a further date. She tested positive to minoxidil diluted in Trichofoam as well as to her her original product - minoxidil and estradiol diluted in Trichofoam. She tested negative results to Trichofoam on its own and estradiol alone diluted in Trichofoam
Is this ALEP or a pustulare contact dermatitis?
The authors propose this is the first reported case of minoxidil-induced ALEP.
The challenge here with this report is really differentiating ALEP from acute pustular contact dermatitis. The authors point out that the pustules here in this case were “non follicular” which points to a diagnosis of ALEP over acute pustular contact dermatitis. It’s hard to tell in the pictures from the author’s manuscript as the pictures are blurry. Some pustules do appear follicular.
Overall, the authors felt that the presence of cervical lymphadenopathy, elevated temperature, and the rapid resolution of skin lesions with subsequent desquamation, following the drug withdrawal, favour an ALEP diagnosis. These findings can also be seen in acute pustular contact dermatitis as well as infected contact dermatitis so it’s hard to say sometimes. We do see cervical lymphadenopathy in contact dermatitis. The rapid resolution is seen in both ALEP and acute contact once suspected agents are removed.
A Word about AGEP AND ALEP
AGEP or “toxic pustuloderma’ is an uncommon type of severe cutaneous adverse drug reaction presenting with non-follicular sterile pustules on the erythematous background. AGEP can be caused by drugs, bacteria and viruses.
ALEP is the localized variant of AGEP! ALEP is rare and only about 25 reports have been published in literature It usually affects the face, cervical region, or thorax. ALEP characteristically presents with onset of localized 1–2-mm sterile pustules 3–5 days after commencement of a culprit drug. Pustules can be larger in some reports. Fever, neutrophilia, and systemic symptoms may or may not be present in the ALEP. However, 42% reported systemic symptoms.
Most cases of ALEP are drug induced (90%). ALEP has been seen with various antibiotics such as amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, levofloxacin. Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), cancer drugs like docetaxel, and sorafenib, itraconazole and finasteride have been associate with ALEP. These were all taken orally. Most cases of drug-induced ALEP are females above 17 years of age.
The pathogenesis of AGEP and ALEP are largely unknown. It is proposed that ALEP is mediated by drug-specific T-cells that cause a type IV reaction. Drug-specific activation of CD4 + and CD8 + T-cells leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis causing vesicle formation. It is propose that vesicles transform into pustules due to release of chemokines like IL-8, IL17 and Il-22
Treatment is stopping the drug. Topical steroids and antihistamines help.
Criteria for ALEP
A few criteria have been put forth for ALEP.
Ryder and Perkins in 2017 proposed the following criteria for ALEP
Localised numerous small (1–3 mm) clustered non-follicular pustules.
Background erythema.
Negative microbiology.
Acute onset (<72 h) after medication.
Resolution (with post-pustular desquamation) within 14 days of discontinuing medication.
EuroSCAR Study for AGEP
A scoring system has been proposed from EuroSCAR Study for AGEP is often applied to ALEP (Sidoroff A et al, 2001). These include the following. A score of 8 -12 is consistent with definite AGEP
a) Presence or absence of pustules (score 0, +1 or +2)
b) Erythema (score 0, +1 or +2)
c) Distribution (score 0 if atypical, +1 or +2)
d) Absence of mucous membrane involvement (score 0 if correct or -2 if not)
e) Acute onset (score 0 if yes or -2 if not)
f) Resolution in 15 days (score 0 if true or -2 if not)
g) Fever more than 38C (score 0 or +1)
h) PMNs more than 7000/mm3 (score 0 or +1)
i) Typical Histology (score -10 to +3)
A score of 0 is no AGEP; 1-4 means possible AGEP, 5-7 is probable AGEP, 8-12 is definite. The full scoring system can be found in this link.
In this study, the patient’s score would be a 6 meaning “probable ALEP” if we use these criteria.
REFERENCE
Makris M et al. Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP) Caused by Topical Application of Minoxidil. J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 20;12(3):831.
Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Vaillant L, Roujeau JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) – a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:113–119.
This article was written by Dr. Jeff Donovan, a Canadian and US board certified dermatologist specializing exclusively in hair loss.