Folliculitis Decalvans: What are the treatment options?
What is Folliculitis decalvans (FD)?
Folliculitis decalvans is a type of scarring alopecia (cicatricial alopecia) which has the potential to lead to permanent hair loss. Diagnosis can be challenging in the early stages of the disease as it can closely resemble dandruff or folliculitis. It’s not clear how common the condition is but it likely affects 1:10,000 - 1:25,000 adults. The exact prevalence still needs to be worked out.
Both men and women are affected by the disease. The disease often starts in the crown with pimple like eruptions and pustules and sometimes bleeding as well. The condition can lead to progressive hair loss. Affected patients may have significant itching, burning and pain.
What is the precise cause of folliculitis decalvans?
The cause of FD is unknown. Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus may play a role for some patients. New research suggests that the bacteria may hide or evade the immune system through creation of biofilms in and around hair follicles.
How is FD diagnosed?
Folliculitis decalvans can usually be diagnosed by visual inspection by an experienced physician. In some cases, a small 4 mm punch biopsy of the scalp may be needed to confirm the diagnosis - especially in early disease states or when the condition closely mimics other conditions like lichen planopilaris or psoriasis or dissecting cellulitis.
Usually though, a clinical history of scalp itching, burning or pain together with clinical findings of pustules and crusts and fusion of hairs to form ‘tufts’ will be highly suggestive of the diagnosis.
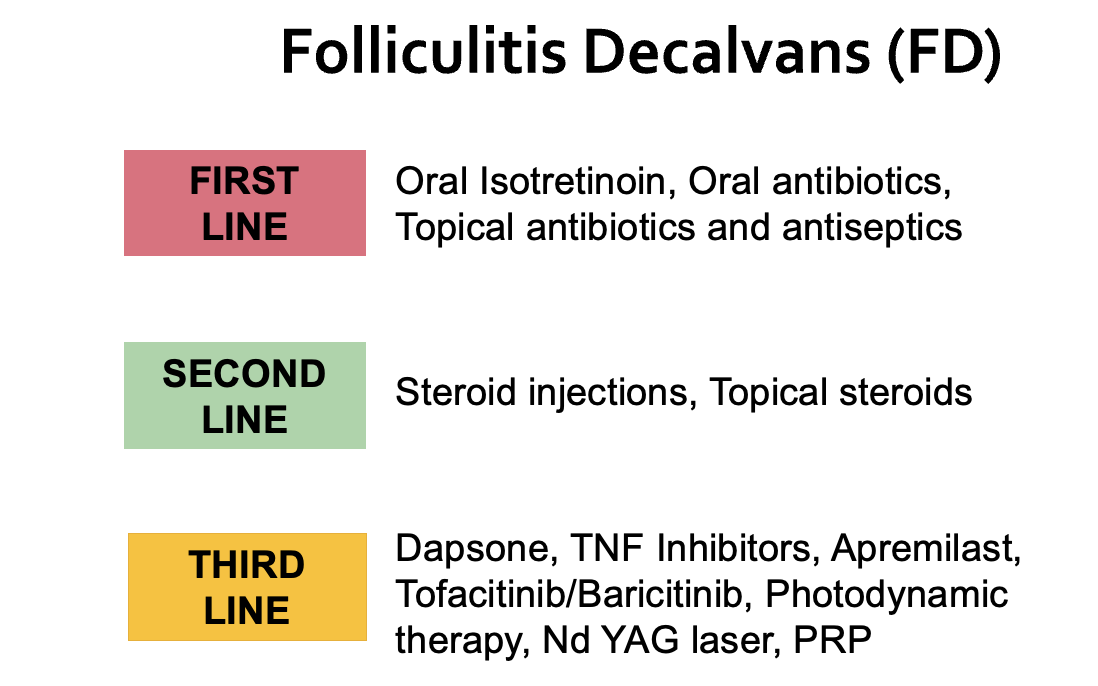
What are the possible treatment options for folliculitis decalvans?
Treatments are divided into first-line, second-line and third line treatments. First line treatments are those which are often used first. Second line agents are those that are used second (if the first line options do not work). Third line options are options that are commonly used for patients that have not had success with any of the first line or second line agents.
Oral antibiotics and oral isotretinoin are the first line options for folliculitis decalvans. Oral antibiotics are often chosen based on the precise bacteria that is cultured when a swab is taken from the scalp. Oral antibioitcs include cephalexin, doxycycline as well as clindamycin and rifampin.
Oral isotretinoin is another first line agent. This is not an antibiotic but rather a pharmacological type of vitamin A.
Treatment may be required long term in order to halt the disease. Not everyone requires long term therapy but many patients do. It is not uncommon for patients to require 12, 24 or 36 weeks of continuous antibiotic therapy before attempting to reduce therapy. Decisions on therapy are complex and require consultation with a dermatologist experienced in the treatment of these conditions.
Second line agents include topical steroids and steroid injections. These can be helpful for some patients and do not generally promote further bacterial proliferation.
Third line agents are less well studied but include dapsone, TNF - inhibitors, JAK inhibitors, apremilast, photodynamic therapy and Nd-YAG laser therapy.
Conclusion
Folliculitis decalvans is a scarring alopecia that requires long term treatment in most cases. Antibiotics or oral isotretinoin are common starting points for treatment. These are considered the first line agents. Patients who don’t respond to the first-line agents move on to second line and third line agents.
This article was written by Dr. Jeff Donovan, a Canadian and US board certified dermatologist specializing exclusively in hair loss.