Increased Histone Deacetylase Activity in Alopecia Areata: Is this a New Avenue for Therapy?
Increased HDAC1 Activity Found in Alopecia Areata
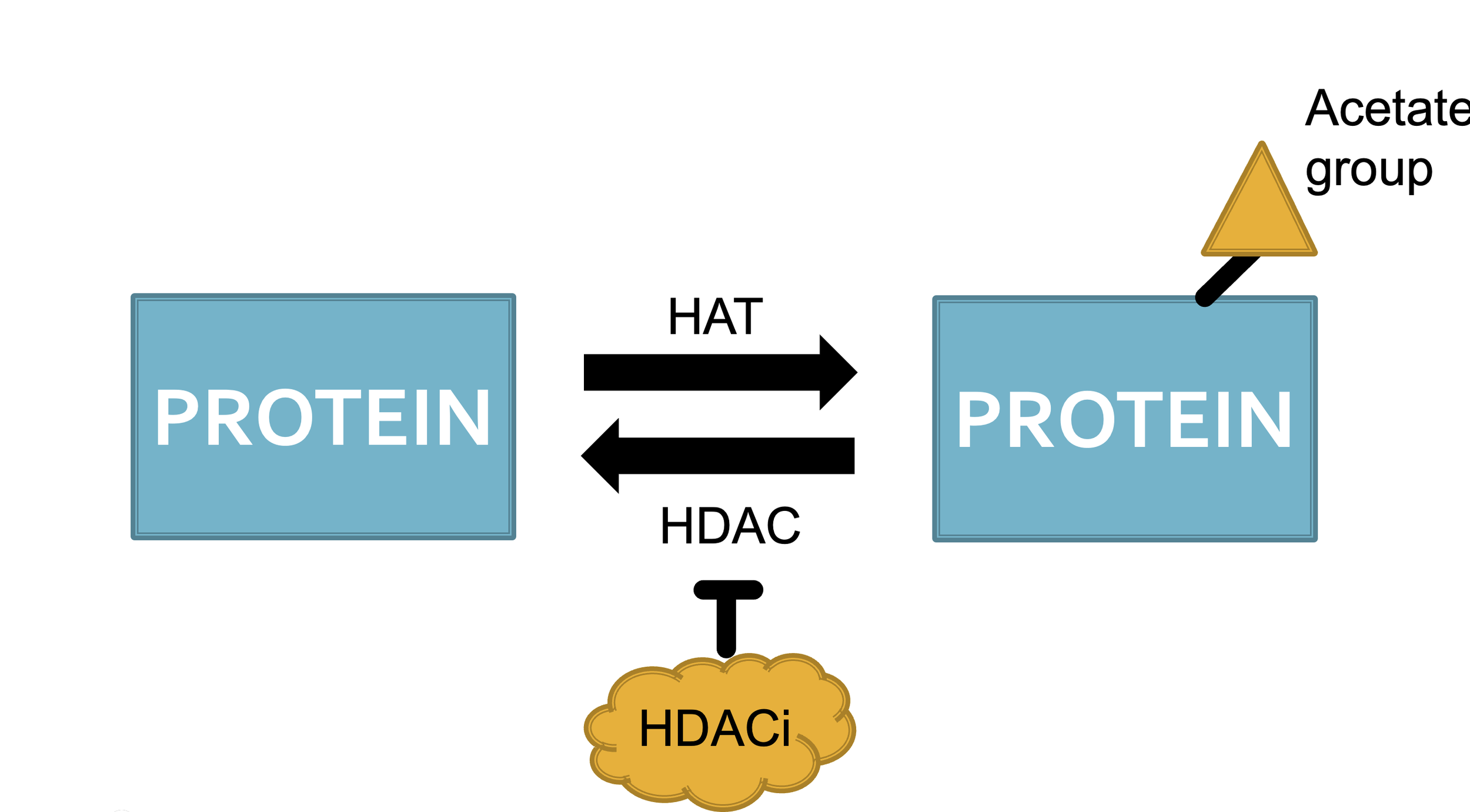
Histone acetylases and histone deacetylase are enzymes that are involved in the additional and removal, respectively of acetate groups from proteins. Such proteins include histone as well as non histone proteins. By controlling the acetylation of proteins, a cell is able to control what genes get expressed and ultimately what proteins get made.
Histone deacetylases have an important role in the skin as well as in the immune system. HDAC1 and HDAC2 are found in the skin and hair follicles and play a key role in embryonic ectoderm development. Researchers have found some epigenetic modifications in form of increased histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) or decreased as HDAC2 and HDAC7 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).
In a new study, researchers set out to determine if there is a difference in HDAC1 deregulation in alopecia areata and acne vulgaris. To do so, the performed a case-control study on 76 participants including 25 patients with patchy alopecia areata, 26 patients with acne vulgaris and 25 healthy controls. Blood samples were collected for the measurement of HDAC1 level by ELISA.
Results are shown in the Table below. Patients with alopecia areata had greater HDAC activity compared to acne patients
Conclusion
This study is interesting as it highlights the increased HDAC1 activity in patients with alopecia areata.
A very long list of drugs that act as HDAC inhibitors exist. Some like Vorinostat, Romidepsin, Panobinostat and Belinostat are approved by the FDA for treatment of some types of cancer. OThers like valproic acid are used in treating seizures adn other neurological disorders. The side effects and/or costs of these drugs would prohibit current use of the main approved HDAC inhibitors for now. However, a large number of drugs that have HDAC inhibitory properties do exist and more studies can confirm whether this is an effective strategy for treating alopecia areata.
REFERENCE
Abdelkader HA et al. Histone deacetylase 1 in patients with alopecia areata and acne vulgaris: An epigenetic alteration. Australas J Dermatol. 2022 Jan 25.
This article was written by Dr. Jeff Donovan, a Canadian and US board certified dermatologist specializing exclusively in hair loss.