Top 10 Things You Need to Know about Oral Minoxidil for Hair Loss
Oral Minoxidil: Top 10 Points for Prescribers and Patients.
Here are the top 10 points that prescribers and users of minoxidil need to know.
1. Oral minoxidil is not FDA approved for hair loss.
The use of oral minoxidil is FDA approved for high blood pressure. Its use in hair loss is entirely off label.
2. If you are going to use or prescribe oral minoxidil, you need to know a thing or two (or three) about it - including who should not be prescribed the drug.
If one is going to use or prescribe oral minoxidil they need to know everything about it. The same is true for any treatment - prescription, non-prescription, cosmeceutical, holistic, natural or ayurvedic. No treatment should be used without solid understanding of risks and benefits, indications and contraindications. If you can’t list 5-6 common side effects of oral minoxidil, I believe you should not be using it or should not be prescibing it. Plain and simple.
One should also have a clear sense who should not use this medication. The following are contraindications or reasons not to be using or prescribing minoxidil:
1. Minoxidil should not be used if women are pregnant or trying to conceive.
2. Patients over 60 years of age can use oral minoxidil only with caution as they may be more sensitive and could potentially have underlying cardiovascular disease which can precipitate angina if blood pressure were to drop.
3, Patients with underlying chronic health issues, especially kidney, heart and liver problems should not use
4. Patients with heart disease include those with previous heart attacks but also those with angina, heart failure and rhythm problems should not use
5. Patients with pheochromocytomas should not use oral minoxidil
6. Patients with porphyria should not use oral minoxidil
7. Patients who have not used or considered other standard hair loss treatments first should not jump not necessarily jump into using oral minoxidil.
8. Patients with low blood pressure to begin with or those using other anti-hypertensives may not be ideal candidates for oral minoxidil. This needs careful review.
3. Oral minoxidil can be a very helpful second-line treatment for many conditions when used properly. This includes androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, chronic telogen effluvium, traction alopecia and post-chemotherapy permanent induced alopecia.
As mentioned above, oral minoxidil is not FDA approved for hair loss. Oral minoxidil can help some conditions and can have an amazing role in managing various conditions. However, it is rarely a first-line agent. Other options might be considered first for many of these conditions, including consideration given to topical 2 or 5% minoxidil. However, if various first-line treatments do not prove completely helpful or can not be used for various reasons, oral minoxidil might be considered. Oral minoxidil at doses 0.25 to 5 mg has shown benefit in treating androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, chronic telogen effluvium, traction alopecia and post-chemotherapy permanent induced alopecia.
4. When minoxidil pills are taken by mouth, most of the drug is quickly absorbed into the blood.
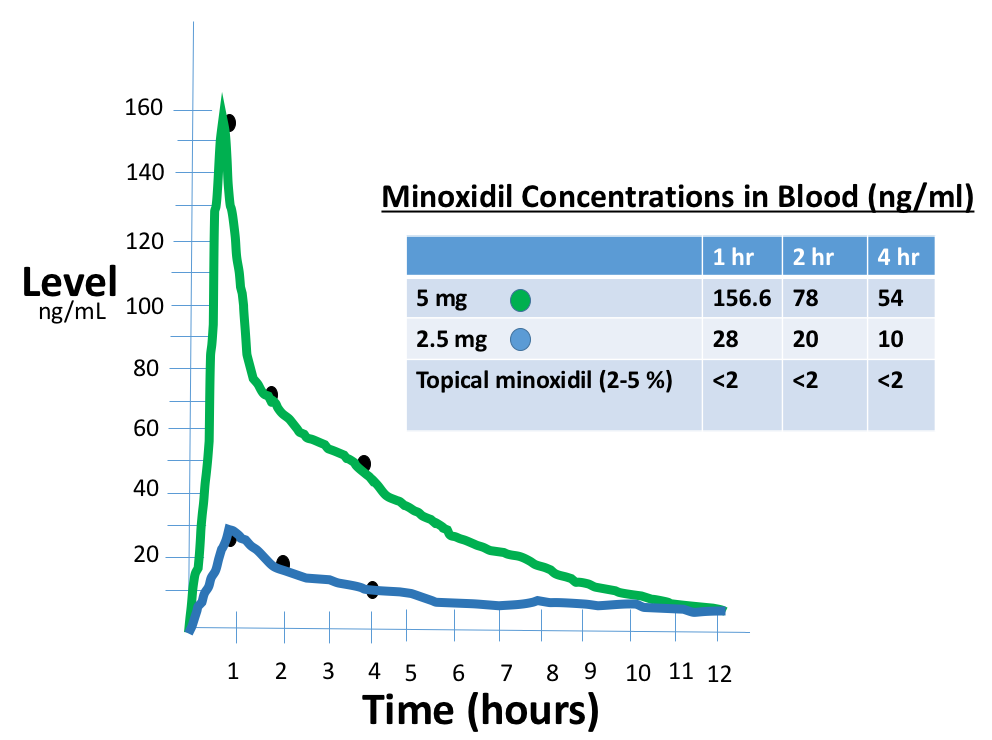
Oral minoxidil is easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The peak levels in the blood occur at around 1 hour after taking the medication and then levels slowly drop after that. Minoxidil is metabolized by the liver. The half life of oral minoxidil is around 4.2 hours. The concentration of minoxidil that appears in the blood depends on the dose used. With 5 mg pills, a concentration of of 157 ng/mL can be measured in the blood about 1 hour later before levels start to drop off. If one-half the amount of minoxidil is ingested (ie a 2.5 mg pill), the concentration in the blood at the one hour time point is actually much less than simply one half the amount. It’s about one-fifth the amount at approximately 28 ng/mL. This is important information because it reminds us that it’s not appropriate to say “Oh you did well on 2.5 mg, I’m sure you’ll do just fine if we go up to a 5 mg dose …. let’s go up on the dose.” Likely the patient will do just fine, but we need to monitor things just the same. There may be more than twice the amount of minoxidil in the blood at certain times with twice the dose. The following image shows my best estimates of minoxidil concentrations at various time points.
5. There are many ‘potential’ side effects of oral minoxidil. The most common ones are easily remembered by the mnemonic “HAIR “- (headaches, ankle edema, increased hair on the face, and rashes/urticaria). Other side effects potentially occur as well.
The headaches may occur from changes in blood pressure. The ankle edema occurs from fluid retention and rarely also manifests with swelling around the eyes. Of course other side effects are also possible, and one needs to understand the range of side effects that can occur. Shortness of breath, increased heart rate and weight gain from fluid retention are all possible.
6. Topical minoxidil does not often change heart rate and blood pressure in most users - but oral minoxidil can.
Studies of topical minoxidil showed that blood pressure and heart rate don’t change significantly in healthy users who use minoxidil at the appropriate dose. That said, there is an occasional patient who does find that their heart rate goes up in the firsts hours after applying minoxidil or that they feel dizzy.
Oral minoxidil can affect heart rate and blood pressure. 0.625 mg doses and 1 mg doses rarely cause changes in blood pressure and heart rate. As we increase the dose, the more and more likely it is for the patient to experience changes. For example, the 5 mg dose is much more likely to cause changes in blood pressure and heart rate than the 2.5 mg dose. We advise our patients to monitor heart rate and blood pressure after starting. (See ORAL MINOXIDIL MONITORING FORM).
7. Although the oral minoxidil reaches peak levels in the blood about 1 hour after a single dose of the pills, the main effect on blood pressure occurs at the 2-3 hour mark and then blood pressure rises again slowly after that. For those using minoxidil daily long term, the maximal effect on blood pressure occurs at the 10-14 day mark.
We generally advise patients to monitor their heart rate and blood pressure weekly after starting. We compare this to baseline measurements to get a sense of the hemodynamic changes (if any) that occur with oral minoxidil use.
ORAL MINOXIDIL MONITORING FORM
It’s helpful to know what is happening to the blood pressure in the first few days but especially 10-14 days after any change in dose. It’s a good idea for users of oral minoxidil to get a baseline blood pressure reading before they start using the pills because one will refer back to this number in future days, weeks and months ahead. Previous studies have taught us that patients using oral minoxidil at doses 0.625 mg and 1 mg rarely have changes in their heart rate or blood pressure after using minoxidil. Changes in blood pressure and heart rate are not that common with 2.5 mg but certainly more common with 5 mg doses. I always advise measuring blood pressure and heart rate initially and then again at the end of the first week and then again at the end of the second and third week. Patients can do this at home themselves if they own a blood pressure cuff or in any local pharmacy (many pharmacies in North America have blood pressure machines that patients can use for free). For most people, there are no changes on the really low doses or oral minoxidil we use for hair growth. Blood pressure should be measured at any time a patient using oral minoxidil experiences dizziness. Fortunately, this is are.
Most studies in the past have shown that it’s once a patient starts using 5-10 mg doses of oral minoxidil that effects on heart rate and blood pressure can be seen. The early studies of oral minoxidil showed that serum concentrations of 21.7 ng/mL was the lowest concentration that resulted in significant blood pressure and heart rate changes in patients. About 1:200 to 1:300 patients using topical minoxidil will achieve this concentration but it’s a bit more common of course in users of 2.5 and 5 mg oral minoxidil.
8. Serum concentrations with oral minoxidil are about 20-30 times higher than topical minoxidil.
It is not surprising that blood levels of minoxidil are higher when you take it orally, but the key question is how much higher? First, it’s important to understand the there is some systemic absorption of minoxidil even in users of topical minoxidil. It’s just that it’s very low. About 99 % of users of topical minoxidil have blood levels less than 2-5 ng/mL. However, some patients using topical minoxidil occassionally do acheive much higher levels or minoxidil in the blood - even levels up to 21 ng/mL. Fortunately that is uncommon. Concentrations of minoxidil higher than 5 % may increase absorption. Topical medications like topical retinoids and topical cortisones can increase absorption of minoxidil for example. The serum concentration of minoxidil is about 20-30 times higher with use of oral minoxidil than topical minoxidil.
9. The higher the dose of oral minoxidil, the higher the levels in the blood.
It may seem obvious but bears mentioning that higher doses of minoxidil lead to greater levels in the blood and the potential for greater side effects. One needs to simply monitor side effects with any dose increase. The potential for side effects for those using 1 mg is greater than 0.5 mg. The chance of side effects for those using 5 mg is greater than 2.5 mg.
10. In addition to the scalp, hair growth on the body occurs in fairly predictable areas if it is to occur.
The eyebrows, hairline, temples, areas under the eyes (malar areas), back of the arms and shoulders are areas outside of the scalp which are most likely to be affected by oral minoxidil use.
About 15-20 % of women using oral minoxidil will experience an increase in body hair including hair on the face. Many users will chose to still continue the minoxidil because they are pleased with its effects on the scalp and remove the excess hair with various means (laser, electrolysis).
Conclusion
Oral minoxidil can be a very helpful second line treatment for many conditions. One must be aware to risks and benefits of this medication and how the risks and potential for side effects change with different doses. IN addition, one needs to be aware to how to monitor patients using oral minoxidil.
Reference
[2] Novak et al. Topically applied minoxidil in baldness. Int J Dermatol. 1985 Mar;24(2):82-7.
[3] Lowenthal DT et al. Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of minoxidil. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1980;2 Suppl 2:S93-106. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198000022-00002.PMID: 6156363
[4] B Canaday. Minoxidil. South Med J. 1980 Jan;73(1):59-64.
This article was written by Dr. Jeff Donovan, a Canadian and US board certified dermatologist specializing exclusively in hair loss.