Evaluating Patients with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): What blood test are important to order?
Evaluation of Hair Loss Caused by PCOS : What labs are important?
Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a common condition in women age 18-44. In fact, about 10% to even as high as 20 % of women in this age group have PCOS. The cause is not precisely known (and likely there are many causes) - genetic, hormonal (high androgens), inflammatory and endocrine (insulin resistance) issues contribute all contribute to the disease.
There is not just one type of PCOS but rather there are many different ways that the condition can present. For this reason, the condition is called a “syndrome”. Most women with PCOS have irregular periods and evidence of clinical or lab evidence of increased androgens. Hair growth on the face (hirsutism), or abdomen, chest, nipples, along with hair loss and acne are common signs of hyperandrogenism in women with PCOS. other symptoms include heavy periods, headaches, darkening of the skin (acanthuses nigricans), skin tags, diabetes, pre-diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol obesity, and infertility. Women with PCOS are at increased risk for cardiovascular disease and uterine cancer.
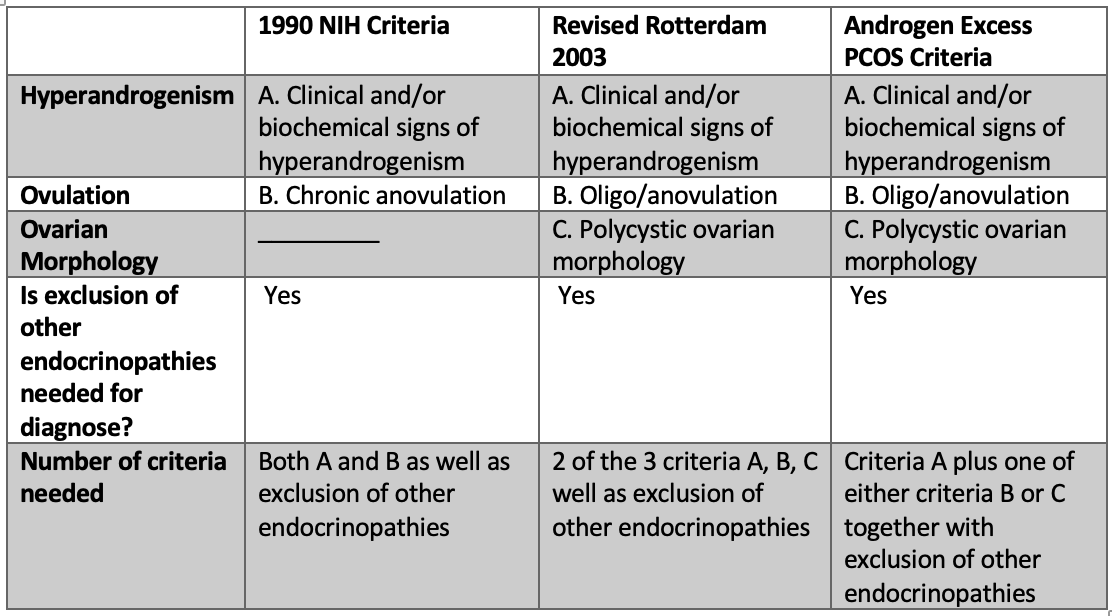
The Criteria for Diagnosing PCOS
The critieria for diagnosing PCOS have been reviewed in a previous post.
What blood tests are needed for patients with PCOS?
Blood tests are needed when evaluating possible POCS for two reasons - two rule out other conditions that mimic PCOS and to evaluate further for the underlying endocrinopathy that defines PCOS. There is no single blood test test that defines PCOS. Rather it is the collection of results that helps solidify the diagnosis and help rule out other conditions.
A variety of lab tests are helpful when evaluating for possibly polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
I typically order the following fasting blood tests on the 3rd to 5th day of the menstrual cycle. If a menstrual cycle has not occurred for an extended period of time, the labs may be taken at any time). Other tests may be important as well depending on the specific patient.
1. Total testosterone, free testosterone - usually elevated; can suppress normal ovulation
2. LH - often elevated; stimulates ovarian androgen production
3. FSH - often normal or reduced
4. LH/FSH ratio - elevated in 75 % of women with PCOS; disrupts ovulation;
5. DHEAS - may be elevated (5 % of PCOS have only elevated DHEAS)
6. Androstenedione - may be elevated
7. Sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) - may be reduced
8. CRP - may be increased and a measure of potentially increased cardiovascular risk in women PCOS
9. ESR - may be increased and a measure of inflammation/metabolic dysfunction
10. CRP/albumin ratio - measure of metabolic dysfunction.
11. Cholesterol levels with triglyceride levels - low HDL, high LDL and triglycerides in some women
12. AST and ALT and bilrubin - elevated in patients with fatty liver and NASH
13. Glucose and hemoglobin A1C - elevated in diabetes and pre-diabetes
14. Urinalysis - abnormal in diabetes and renal diseases
15. Prolactin - elevated in other endocrinopathies such as prolactinomas; mild elevations present in some women with PCOS.
16. 17 hydroxyprogesterone (17 OHP) - elevated in other endocrinopathies such as CAH
17. AM cortisol - elevated in other endocrinopathies such as Cushing’s
18. TSH - elevated or reduced in other endocrinopathies such as thyroid diseases.
19. Estradiol - usually normal but may bee elevated in some women with PCOS; reduced in other endocrinopathies such as ovarian failure.
Other tests may be appropriate in some women in addition to standard tests such as CBC, ferritin:
20. beta-HCG - rule out pregnancy
21. AMH - often elevated in PCOS; low in ovarian failure and premature menopause
22. insulin - elevated in insulin resistance states and stimulates ovarian androgen production
Other tests such as blood pressure, weight, height are important to obtain. A ultrasound of the ovaries may be important to consider in some women as well. An ultrasound examination helps visualize these changes in more than 90% of women with PCOS. It is important to always keep in mind that these ultrasound changes are also found in up to 25% of women without PCOS symptoms.
This article was written by Dr. Jeff Donovan, a Canadian and US board certified dermatologist specializing exclusively in hair loss.