TNF inhibitors for Refractory Dissecting Cellulitis
Adalimumab and infliximab Helped Patients with Resistant Disease
Authors from France performed a multicenter retrospective study evaluate the efficacy of anti-TNF agents in treating dissecting cellulitis after failure of other conventional treatments. Clinical efficacy was assessed using a 5 point Physician’s Global Assessment Scale (PGA), and quantified according to the number of inflammatory nodules, the presence of abscesses. The Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and the severity of pain and the patient satisfaction index (from 0 to 10), were also used quantify clinical efficacy.
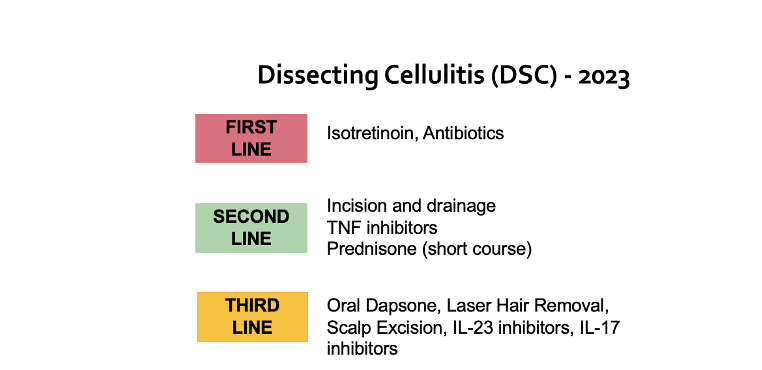
There were 26 patients (25 males and 1 female) included in the retrospective study. The mean age at symptom onset was 24 ± 10 (median 21.5) years. A body mass index of >30 kg/m2 was observed in 42% of patients, 14 patients were smokers (53%), and 3 of them were cannabis consumers. TNF blockers were introduced as a third-line treatment for almost all patients (24/26). Previous ineffective treatments included systemic antibiotics (92%), isotretinoin (65%), and oral corticosteroids (11%).
TNF INHIBITOR AGENTS USED
Five patients were treated with adalimumab (40 mg/2 weeks) and 21 patients were treated with Infliximab starting at a dose of 5 mg/kg every 4, 6, or 8 weeks, increased to 7.5 mg/kg in 6 patients, and to 10 mg/kg in 4 patients.
The mean treatment duration was 19 ± 21 months.
RESULTS
The PGA score decreased from 3 to 1. The median number of inflammatory nodules decreased from 7 to 0.5. The median number of abscesses decreased from 1 to 0.
The DLQI decreased slightly from 10 to 8 and the NRS score for pain severity and 6 to 1.
Overall, the median treatment satisfaction was 7 out of 10.
TNF inhibitors were stopped in 8 of the 26 (31 %) patients. 18 of 26 continued these treatments (69%). Reasons for stopping included optic neuritis, elevated liver enzymes elevation. Two patients were in remission and 3 demonstrated moderate efficacy and stopped. 1 was lost to follow-up.
Comments
This is one of the largest series of TNF inhibitor use of DSC. After treatment with a TNF inhibitor, symptoms and quality of life improved significantly, and the patients were overall satisfied.
It is interesting to note that even though the mean satisfaction index was 7.25 out of 10, the DLQI only dropped from 10 to 8. The DLQI examines effects on quality of life, embarrassment, sexual health, ability of work, ability to participate in leisure and hobbies. It would appear that even though there has been improvement in pain and abscesses, there remains some permeant dysfunction and permanent alteration in quality of life. This speaks to the need for early diagnosis and aggressive treatment.
This data supports the effectiveness of anti-TNF medications in treating DCS in patients who do not respond to conventional treatments. I put it on the list as a second line agent.
Reference
Alzahrani M et al. Treatment of dissecting cellulitis of the scalp with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: a retrospective multicenter STUDY. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2023 Jan 26;llad036.
This article was written by Dr. Jeff Donovan, a Canadian and US board certified dermatologist specializing exclusively in hair loss.